This post is for fellow students who is studying Operations Research with CPLEX. If you don’t know already, IBM offers free academic license for IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio.
First, you have to register IBM Academic Initiative with your academic instituion issued email. (e.g.
foo@university.edu,foo@university.edu.tr)Then, Login and go to here.
Find the “IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio” under Softwares sections.
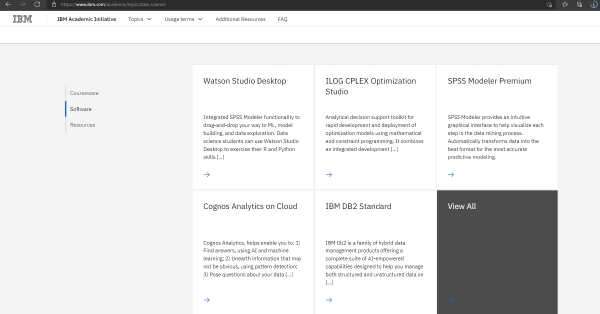
- Navigate to “Downloads”.
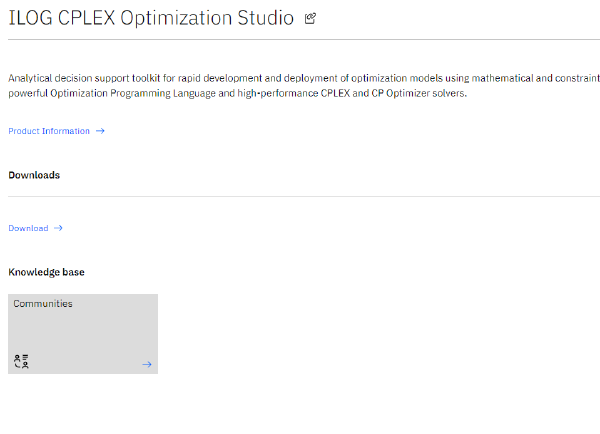
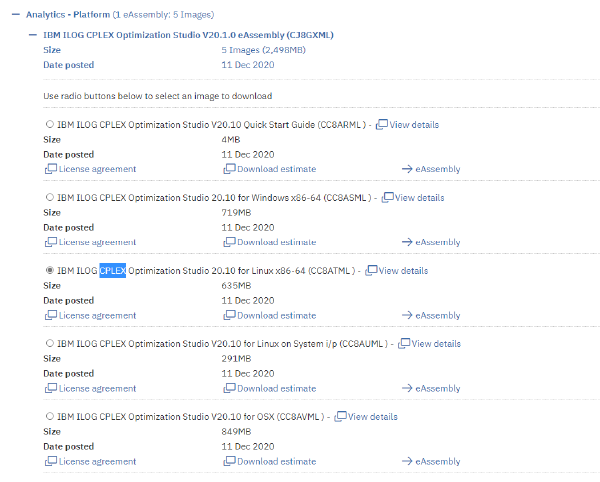
- Find the version that suits your environment and download.
If you are using Windows, you’ll see a GUI, and as usual just click Next, Next.
If you are on Linux, you probably already know how to install a package.
chmod +xto give execute permission to the file.- Then execute it.
./filename - Follow the instructions given by the installer.
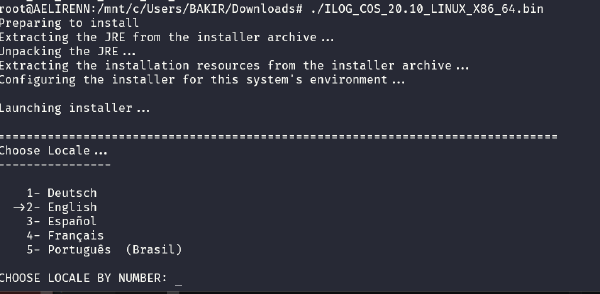
- Now you have installed the Optimization Studio and CPLEX solver with it.
After the installation, you can see the Interactive Shell using cplex command in command prompt.
Of course the Environment Variables must be defined, and it should be automatically (usually after a restart on Windows).
This is not how we are going to use CPLEX though. You can type quit to exit the shell.
In the next post, I’ll share an example about how we can use CPLEX with Python using docplex library.
Before that we must install cplex package for python using the setup.py included in the directory that you installed CPLEX. e.g. C:\Program Files\IBM\ILOG\CPLEX_Studio201\cplex\python\3.7\x64_win64\setup.py
python path_to_cplex\python\setup.py install
